Two common conditions that affect them are THROMBOSIS and varicosities (see below).
are dilated tortuous veins occurring in about 15 per cent of adults – women more than men. They most commonly occur in the legs but may also occur in the anal canal (HAEMORRHOIDS) and in the oesophagus (due to liver disease).
Normally blood flows from the subcutaneous tissues (skin and underlying connective tissue) to the superficial veins which drain via perforating veins into the deep veins of the leg. This flow, back towards the heart, is aided by valves within the veins. When these valves fail, increased pressure is exerted on the blood vessels leading to dilatations known as varicose veins.
Treatment is needed to prevent complications such as ulceration and bleeding, or for cosmetic purposes. Treatment alternatives include injection with sclerosing agents to obliterate the lumen of the veins (sclerotherapy), or surgery; in the elderly or unfit, an elastic stocking may suffice. One operation is the Trendelenburg operation in which the saphenous vein is disconnected from the femoral vein and individual varicose veins are avulsed. (See also VASCULITIS.)
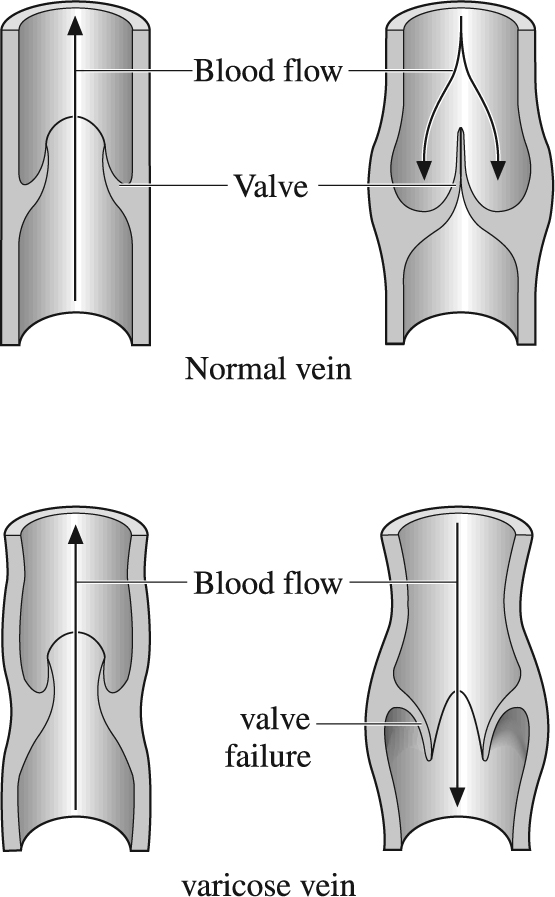
(Top) Normal vein showing how a closed valve prevents back flow of blood. (Bottom) Vein with faulty valve which allows some blood to leak back through the part-opened valve.
Thrombosis (venous thromboembolism or VTE) occurs when blood, which is normally a liquid, clots within the vein to form a semisolid thrombus (clot). This occurs through a combination of reduced blood flow and hypercoagulability (an increased tendency to clot). The most common site for this to occur is in the deep veins of the leg, where it is known as a DEEP VEIN THROMBOSIS (DVT).
Predisposing factors include immobility (leading to reduced blood flow), such as during long journeys (e.g. plane flights) where there is little opportunity to stretch one's legs; surgery (leading to temporary post-operative immobility and hypercoagulability of blood); administration of OESTROGENS (low-dose oestrogen ORAL CONTRACEPTIVEs carry a very low relative risk); and several medical illnesses such as heart failure, stroke and malignancy.
Deep-vein thrombosis presents as a tender, warm, red swelling of the calf. Diagnosis may be confirmed by ultrasound scanning looking for flow within the veins or by venogram (an X-ray taken following injection of contrast medium into the foot veins).
Prevention is important. This is why patients are mobilised and/or given leg exercises very soon after an operation, even major surgery and why it is routine to prescribe fixed doses of low molecular weight HEPARIN post-operatively to help prevent this complication. Car drivers should stop regularly on a long journey and walk around; airline travellers should, where possible, walk round the aisle(s) and also exercise and massage their leg muscles, as well as drinking ample non-alcoholic fluids. In general people should avoid sitting for long periods, particularly if the edge of the seat is hard, thus impeding venous return from the legs.
Diagnosis and treatment are important because there is a risk that the clotted blood within the vein becomes dislodged and travels up the venous system to become lodged in the pulmonary arteries. This is known as PULMONARY EMBOLISM.
Treatment is directed at thinning the blood with ANTICOAGULANTS, initially with heparin and subsequently with oral anticoagulants for a period of time while the clot resolves.
Blocked superficial veins are described as superficial thrombophlebitis, which produces inflammation over the vein. It responds to anti-inflammatory analgesics. Occasionally heparin and ANTIBIOTICS are required to treat associated thrombosis and infection.