A method of recording the electrical activity of the heart muscles. Electrodes from a recording machine (electrocardiograph) are placed on the skin of the chest wall, arms and legs. The record of the electrical changes is called an ECG (ELECTROCARDIOGRAM). The number of electrodes used depends on the complexity of the heart disorder being monitored. The procedure can be done in hospital, doctors’ surgeries and the patient's home, and does not cause any discomfort.
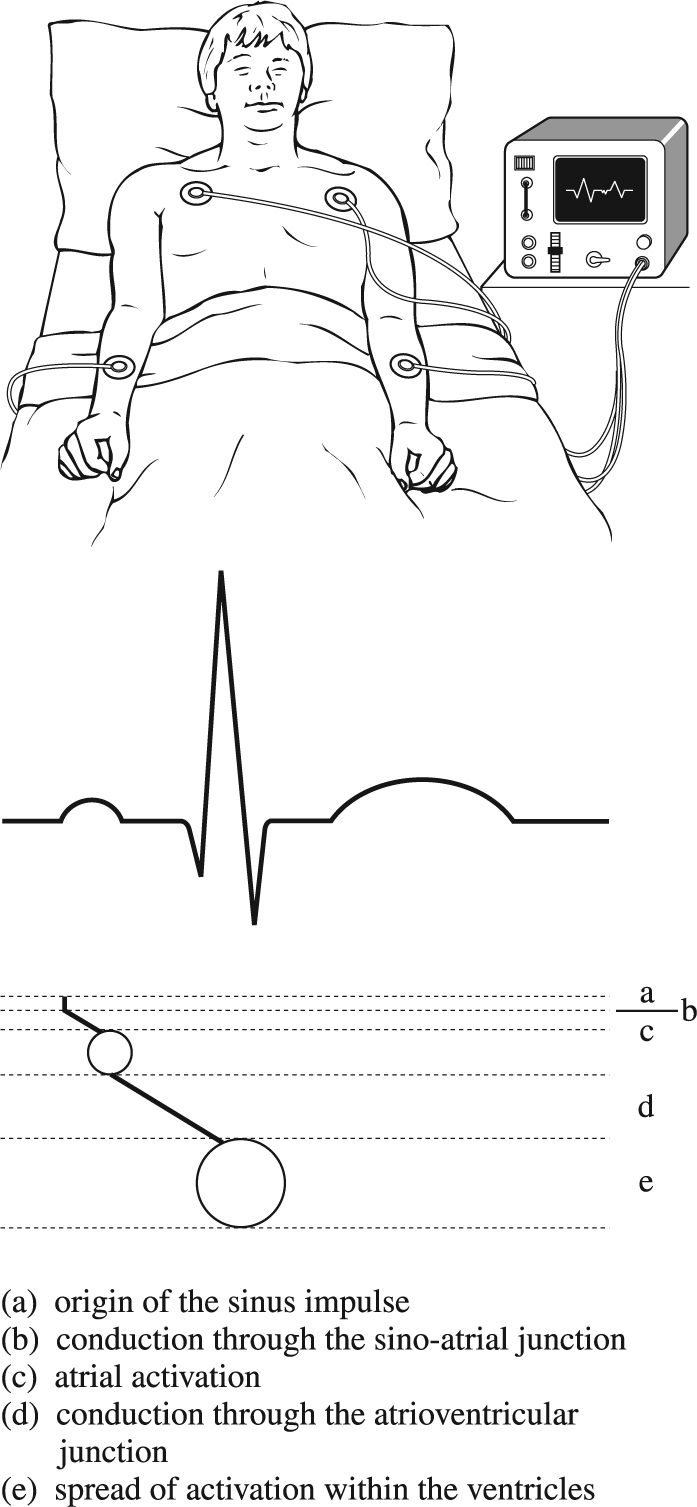
Tracing of normal electrical impulse that initiates heartbeat (after The Cardiac Arrhythmias Pocket Book, Boehringer, Ingelheim).
In certain circumstances – for example, where a person has had bouts of chest pain – an exercise ECG may be performed under medical supervision. The patient walks on a treadmill while the ECG is recorded continuously.